What China’s electric bike charging stations can teach us all


Electric car charging stations are becoming ubiquitous across many cities in the US. But with electric bikes vastly outnumbering electric cars, should we be considering charging stations for these more popular light EVs? In China, e-bike charging stations are already commonplace. Perhaps we can learn something from them.
In fact, I didn’t know just how common these charging stations were in China until recently. I was talking with William Guo, whose company develops and markets e-bike charging adapters for European and US electric car charging stations. Basically, it’s a device that plugs into a car charging station and converts the J1772 or European Type 2 connector into a typical wall outlet for Level 1 charging. That wall outlet can then be used to plug in any standard home charger, such as for an electric bicycle, e-scooter, e-skateboard, or other device.
It’s a great solution for the Western world, but he mentioned that in China where he lives they tend to prefer just using an e-bike charging station, to which I responded “a what now?”
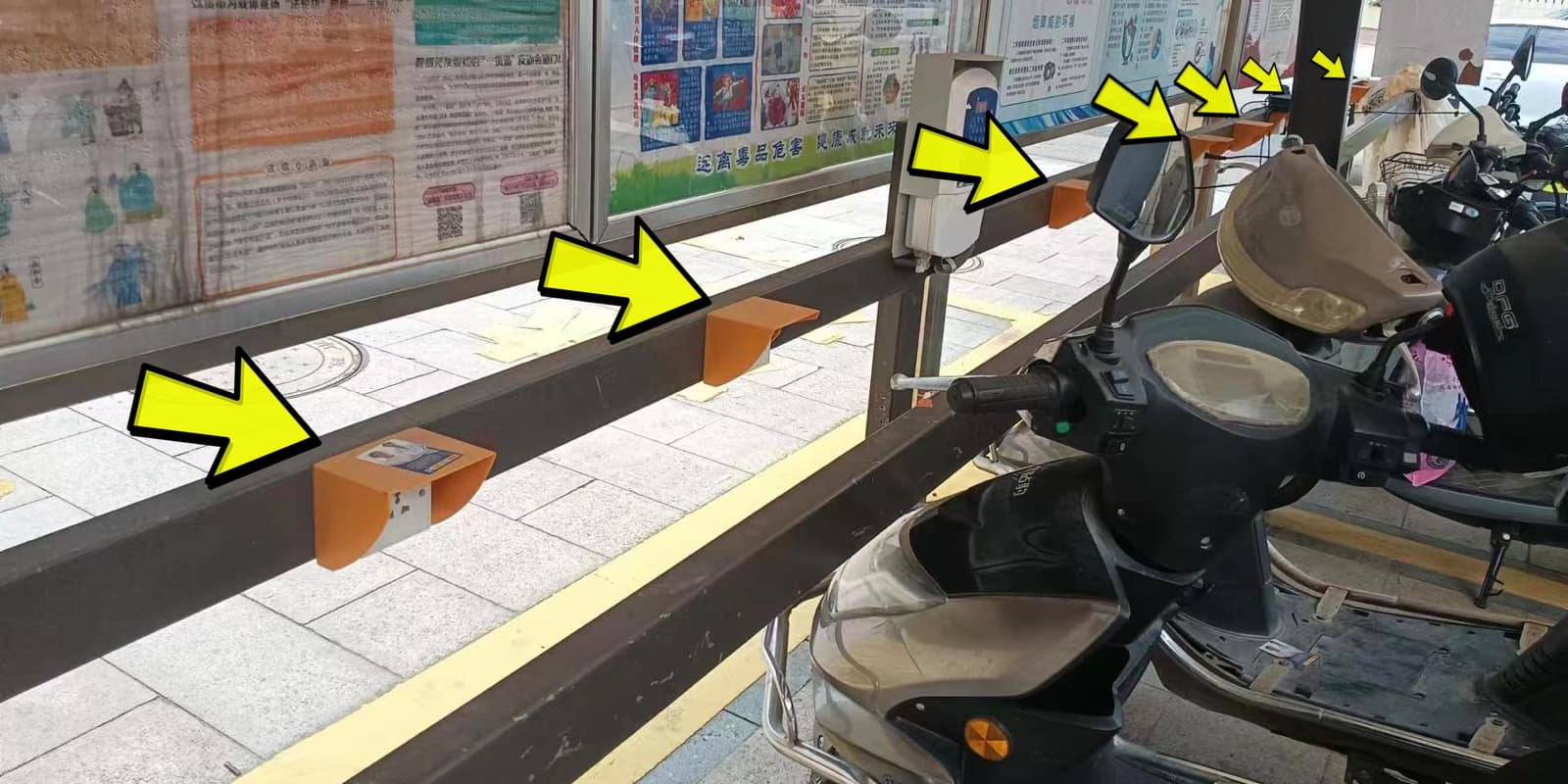
As it turns out, electric bike charging stations are common in China. William sent me some photos of an e-bike charging station near where he lives in Zhejiang Province, as well as a few others around town.
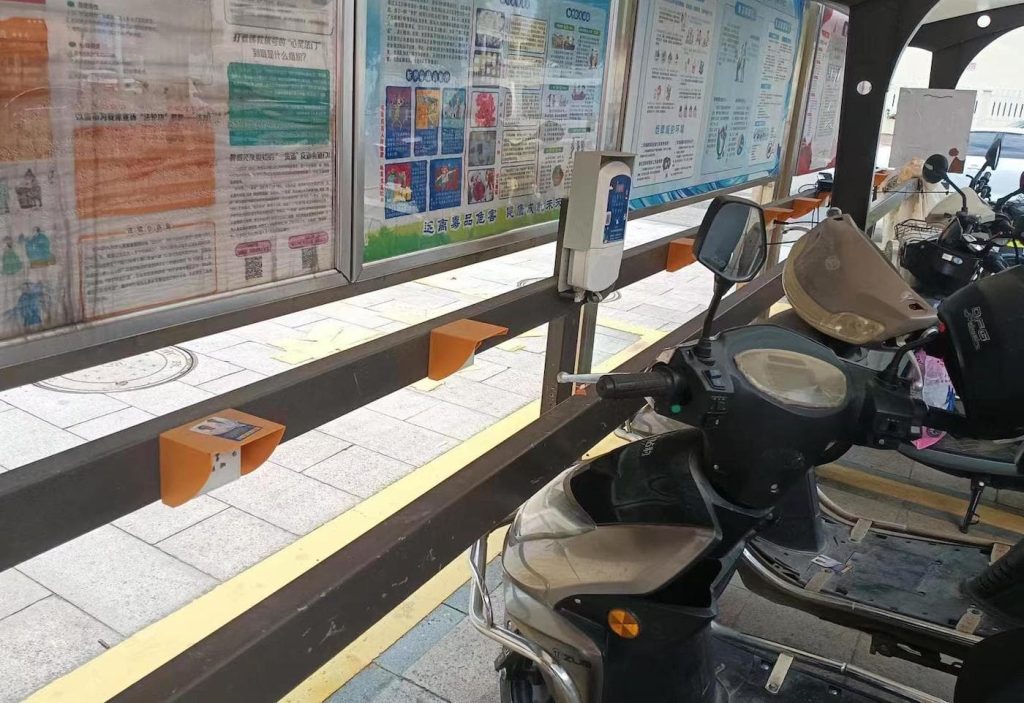


I actually visited Zhejiang Province in 2019, but I never saw stations like these.
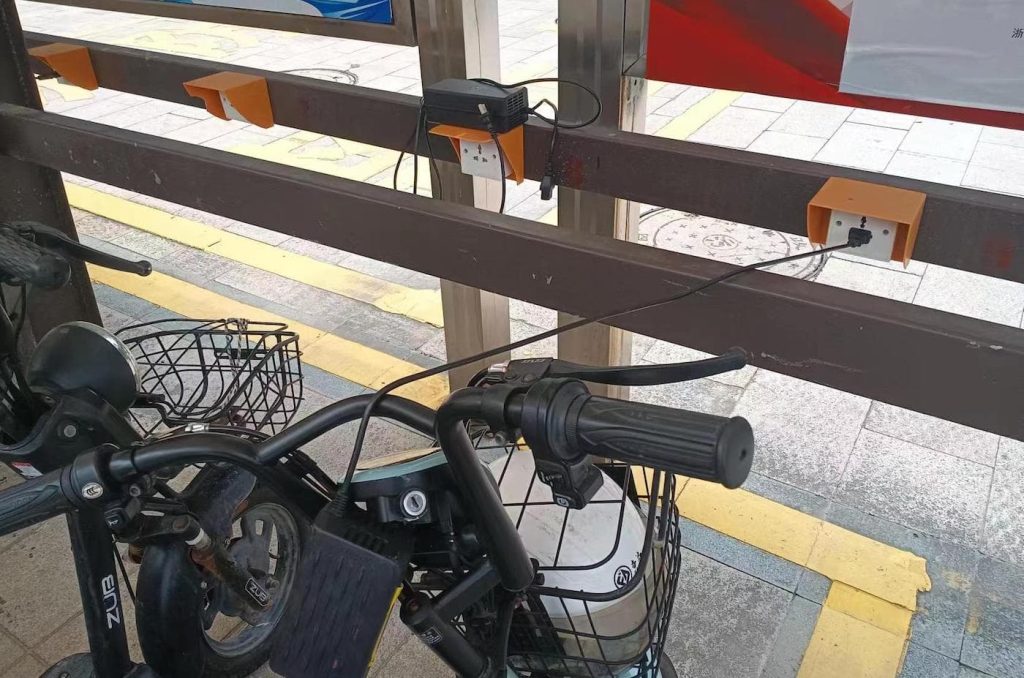
There are a few designs but most are variations of a simple concept: a row of wall outlets connected to some type of payment portal.
Riders generally carry their charger with them so they can plug in at a charging station near work or any other destination. Electric bicycles in China are frequently more of a moped or scooter-style design, meaning they have more storage options on the bike that make it easier to carry the charger with them.
I asked William if riders weren’t worried about someone stealing their charger while they’re charging. “Charger theft isn’t really a problem,” he responded. “They just aren’t worth much.” It makes sense to me, especially considering a new e-bike charger on Amazon can be had for $20-$35. Considering they come from China anyway and who knows what the markup is by US importers, the local price must be pretty darn low.
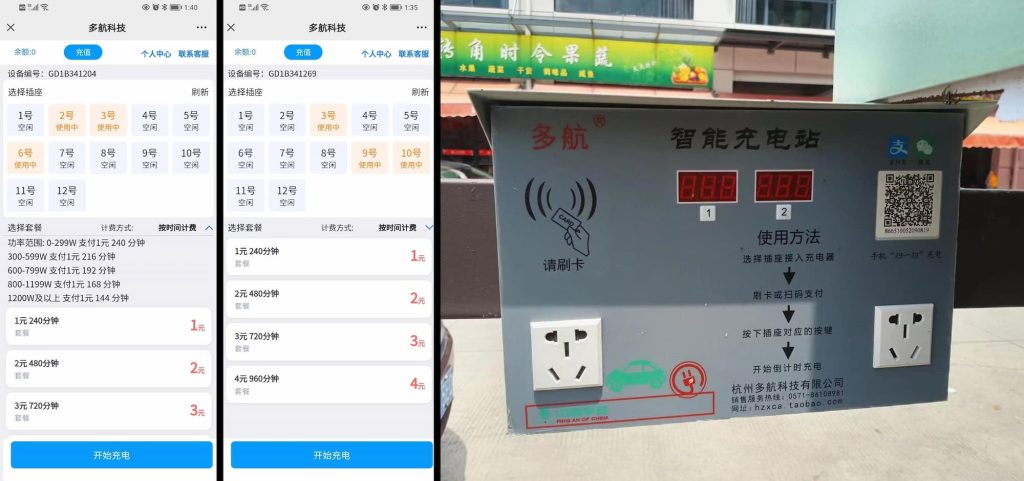
William also shared with me some screenshots from the charging station app, showing the various charging options and which charging outlets are still available at any moment.
The prices are based on charging time and charging power, but seem quite reasonable. For example, a 240-minute charge at under 300W costs just 1 RMB (US $0.14). For comparison, most e-bike chargers in the US are rated at around 150-250W.
Higher power is available from the station, which would likely be used on heavier moped-style e-bikes than the type of e-bikes we generally see in the US or Europe. A 1.2 kW charger would run for about 144 minutes for the same price. Users can also pay 2 or 3 RMB (US $0.28 or $0.42) for twice or three times the charging time, which would basically cover an all-day charge.
There are other types of e-bike charging stations in China that actually have the chargers built into the machine and are better suited for those that don’t carry their charger with them. Still other designs have several AC power cords that directly plug into the charger, meaning riders can plug their chargers into that cord. That design also likely deters folks who want to use the station to get a quick charge of their phone or laptop from an AC outlet, since you don’t have a typical wall outlet on the face of the machine.
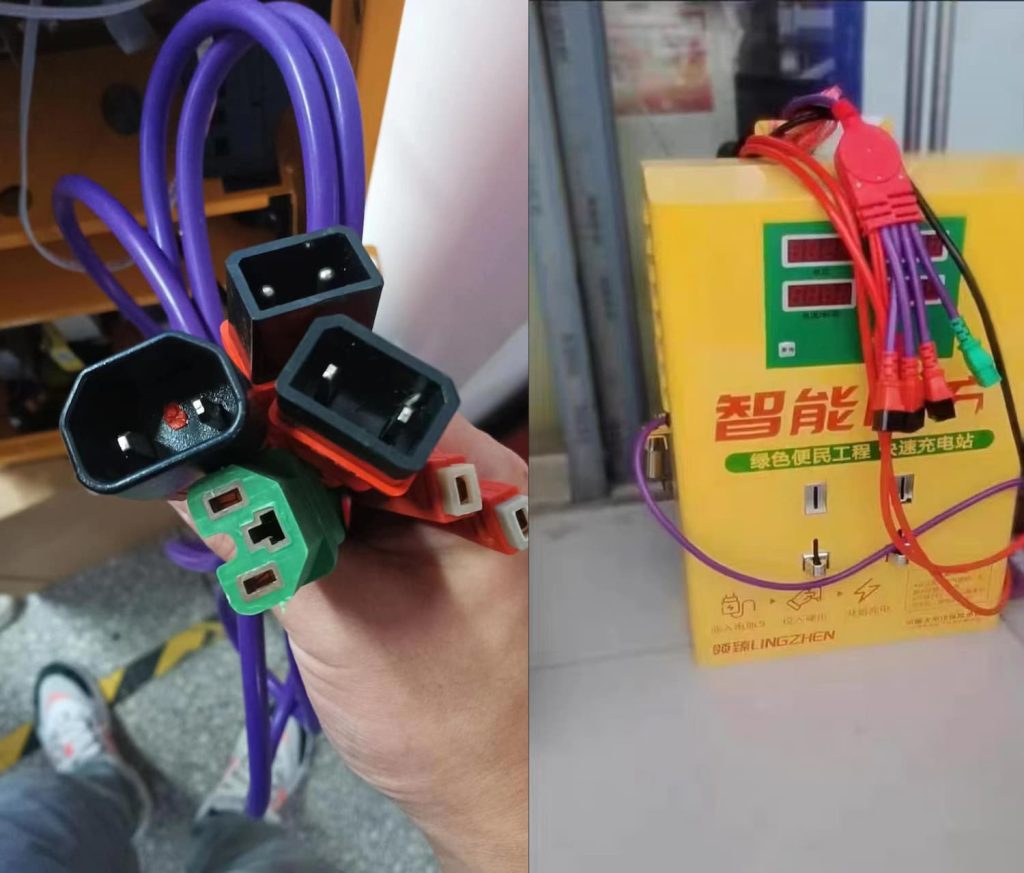

All of this goes to show just how simple electric bike charging stations can truly be. Ultimately, these are just glorified extension cords with a payment portal. That’s all you really need.
And perhaps that’s the biggest lesson of all here. If we want to make it easier for people to commute by electric bike, especially over longer distances, such simple e-bike charging stations can be a great idea. It’s not totally foreign in the US. We’ve seen examples in Oregon and New York. But those are the exception, not the rule.
Today’s throttle-controlled electric bicycles with lithium-ion batteries often have ranges of between 20-30 miles (32-50 km) when new, but that range can drop after several years. Being able to charge up while at work is a great way to avoid needing to replace a functional battery that still has a few years of use left despite not holding as much charge as it used to.
Centralized charging locations can also help combat the issue of e-bike fires in the US. It’s important to point out that e-bike fires are extremely rare. You hear about them often on the news because of the old “if it bleeds, it leads” adage. Every day hundreds of thousand of e-bikes get charged in the US without any fires. But occasionally fires due occur, often during charging, and so it is still an important issue to consider when planning for safe e-bike charging.
Having a centralized charging station for e-bikes that is outside of people’s homes or workplaces helps improve safety. Such stations can even be fitted with an appropriate fire suppression system in the ceiling, just in case.
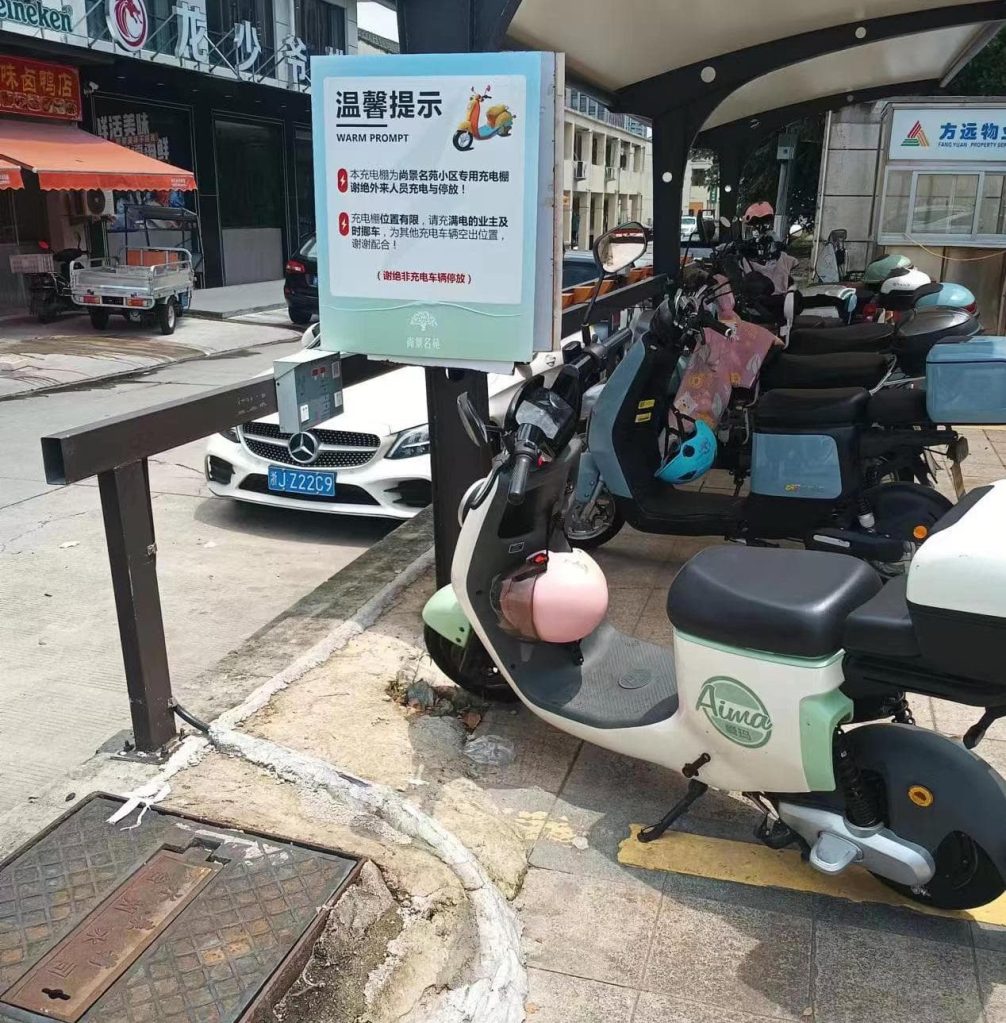

While the US use case for e-bikes isn’t quite the same as in China where e-bikes are used by a huge swath of the population as primary vehicles, there are still plenty of people in the US that could make use of e-bike charging stations.
And when they’re this simple to set up, perhaps it’s something more places should be considering. They’d be useful for more than just electric bikes, but also Vespa-style electric scooters and even electric motorcycles that don’t have typical charging station connectors.
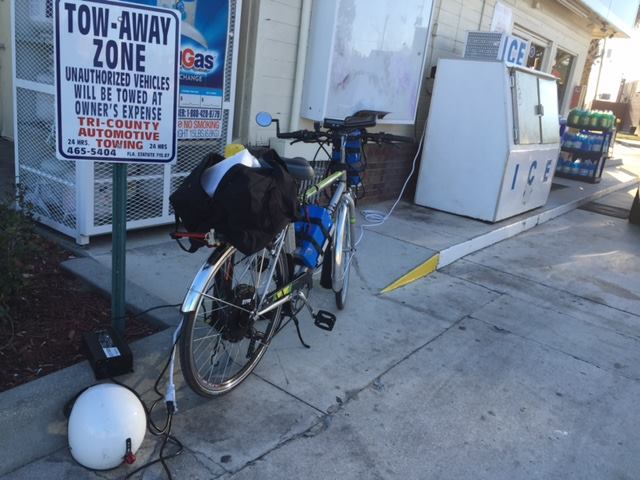
Just for fun, I’ll leave you with an image from 2015 when I did a 500-mile (800 km) trip on a DIY electric bike and I had to find places to charge along the way (despite having a massive 2.8 kWh of battery on the bike).
Pro tip: look for vending machines and ice machines. In a pinch, they’ll lead you to an outlet. Buying something from the place you “borrow” $0.30 of electricity from is a nice gesture, too.

FTC: We use income earning auto affiliate links. More.